Digital lending in India is growing at an explosive pace. The market stood at a record USD 270 billion in 2022 and is set to reach USD 350 billion by 2023.
Reports show that 52% of Indian adult consumers are active digitally and use fintech. The rise of digitally active adult consumers and a rapidly expanding ecosystem of digital lending applications have accelerated digital lending in the Indian market. Technological innovations, elevated customer experiences, and faster loan disbursals have propelled the growth of this industry. The current potential opportunity is approximately INR 12 trillion. This is expected to reach an opportunity of approximately INR 104 trillion by 2030.
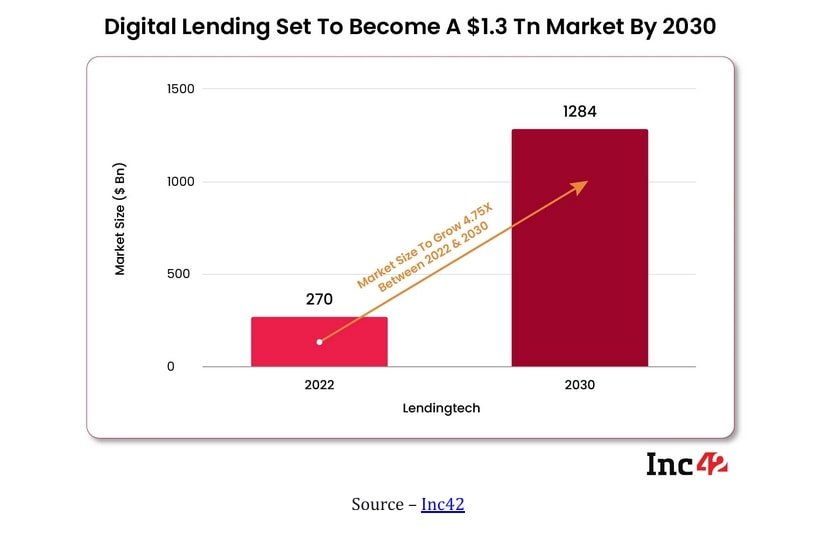
Digital lending actively caters to the non-banking population or those new to credit. Many start-ups and NBFCs are entering the market to cater to Millennials, Gen Z, underserved communities, and rural demographics who were often refused loans owing to low credit scores. Growing smartphone proliferation and internet access have also propelled the rise of digital lending in India.
The Role of Infrastructure in Digital Lending
The rate of technological development in this space is also expanding as more players enter the digital lending market with differentiated offerings of their own that leverage the power of digital technology. For instance, now there is a growing focus on the use of AI to increase business profits in digital lending by automating and streamlining the business process, making intelligent recommendations, or driving customer self-service using chatbots is on the incline. Leveraging process automation for functions like payroll and assets, verifying data and identity information, flagging incomplete data, etc., to elevate the lending experience is also increasing.
Digital lenders are also using the power of the cloud for better service delivery, facilitating easier document management, and sharing and elevating data processing capacities. Along with this, there is a hyperfocus on cybersecurity to maintain information and data integrity and prevent new threats, such as synthetic fraud or other potential cyberattacks. The RBI has mandated clear guidelines to protect customers’ data and lower the otherwise increasing number of frauds in the system.
But these wheels will only keep turning when the ecosystem supports these growing demands of digital lending. This is easier said than achieved. For instance, major complexity arises because new technology applications and processes live in the same ecosystem as legacy applications. Evaluating the strengths and abilities of the entire ecosystem, as such, becomes imperative.
For the growth of Digital Lending, the ecosystem needs to be built for :-
Performance
One of the key reasons for the rise of digital lending has been the ease of loan application and disbursal. As the demographic leveraging digital lending expands and also rises in digital sophistication, their need for more seamless experiences increases. Engineering digital lending platforms and applications for performance as such becomes a critical goal.
Performance engineering takes care of all the variables that impact platform or application performance. This includes the network demand, application and infrastructure considerations, and engineering applications to deliver a fast user experience.
Performance engineering of the infrastructure also ensures high productivity for both employees and external users, allowing organisations to maintain their Quality of Service.
Availability
The availability of digital lending applications and platforms is key to their success. Digital lending applications, for example, are being used by the rural population. Infrastructure considerations here must account for several checkpoints specific to the demographics. High internet strength and bandwidth, for example, cannot be considered a given in rural areas. Applications, consequently, must be engineered to operate or update even within low bandwidths.
The deliberations on application architecture and back-end infrastructure become critical since legacy and business-critical applications to cloud solutions and off-the-shelf application suites live in the same ecosystem. The infrastructure, as such, needs to be seamlessly integrated to drive availability and performance and capably navigate large volumes of complex touchpoints across departments and applications.
Measuring the service demands of various systems and identifying complex issues across the technology stack, e.g., connection leaks, network bottlenecks, thread contentions, database holder events, server crash events, high CPU utilisation issues, etc., are crucial here.
Security
Security must now move from a reactive to a proactive stance with the burgeoning of digital lending. Reports show that the sophistication and volume of cyberattacks in the BFSI sector have been on an incline. Developing robust security protocols and creating a fool-proof and manipulatable security architecture as such become non-negotiable. Along with this, assessing the current security capabilities of the application and digital lending ecosystem are also crucial to adopt a preventive security approach.
Developing predictive capabilities for early detection of issues, continuous improvement in the Quality of Service (QoS), and automated issue analysis emerge as critical capabilities. The abilities to isolate problematic applications quickly, create event-based triggers, and have a continuous view of the health of various applications in the IT system are also indispensable for application security.
Scalability
Scalability ensures that application performance is not impacted even when the number of concurrent users increases. Scalability is an essential contributor to customer experience as it influences the user experience. It’s driven by several factors and can be harder to implement in complex integrated environments.
Therefore, it’s imperative for digital lending platforms to unlock the complexities of integrated applications that use heterogeneous technologies in multi-vendor scenarios and account for all technology, system, and network demands for scalability.
So, What’s the Way Forward for the Indian Digital Lending Ecosystem?
The consumer today, whether rural or urban, is familiarising themselves with elevated, streamlined, and secure digital experiences. Taking stock of the tech ecosystem supporting the digital lending platform becomes a critical first step to success.
Identifying performance bottlenecks and resolving all Performance, Availability, Scalability, and Security (PASS) issues across the technology stack are essential. Additionally, these performance validation activities cannot be limited to testing the system alone. The test results must provide an engineering analysis of the test results to identify performance bottlenecks, areas of improvement, and predictive metrics.
Because you can only manage what you can measure, comprehensive performance benchmarking to measure whether the application meets all current and future requirements becomes a critical cog in the wheel here.
Strategies such as NFR formalisation and prioritisation are important to optimise infrastructures, identify application architecture gaps and identify the risks, trade-offs, and sensitivities in the architecture.
These activities not only help in addressing the needs of complex hyper-scale applications but also allow organisations to create inherently scalable and secure architectures that can meet current and future business demands.
Connect with us to see how Avekshaa can optimise your digital lending platform and help you rapidly isolate, address, and solve all PASS issues across the tech stack, proactively engineer your applications for performance, and continuously improve the Quality of Service (QoS) to prevent issues and downtime.


