Key Takeaways:
- NFV (Network Functions Virtualization) virtualizes traditional network devices, enabling flexible, cost-efficient, and software-based network functions.
- CNFs (Cloud-Native Network Functions) extend NFV by using containers, microservices, and cloud-native architectures for faster deployment and better scalability.
- Deployment difference: NFV uses virtual machines, while CNFs rely on lightweight containers for efficiency.
- Architecture difference: NFV often uses monolithic VNFs; CNFs are microservices-based, allowing independent updates and scaling.
- Performance & agility: CNFs provide faster deployment, higher scalability, and improved resource utilization compared to NFV.
- Modern network benefits: CNFs enable rapid service rollout, high reliability, automation, and cost optimization.
- Challenges: Migrating from NFV to CNFs may require planning, new skills (Kubernetes, containerization), and updated orchestration tools.
- Future-ready networks: CNFs support technologies like 5G, edge computing, and AI-driven network automation.
- How we help: Partnering with us ensures smooth adoption of NFV and CNFs, reliable network monitoring, and optimized cloud solutions.
- Strategic advantage: Leveraging CNFs allows organizations to build agile, high-performance, and future-ready telecom infrastructure.
The telecom industry is evolving rapidly, and modern networks need to be flexible, scalable, and reliable. Two important innovations in this space are Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) and Cloud-Native Network Functions (CNFs). Both technologies aim to improve network performance while reducing costs and complexity, but they approach this goal differently.
At our company, we help organizations adopt modern network infrastructure while ensuring reliability, performance, and smooth operation. In this blog, we’ll explain the difference between NFV and CNFs, how they work, and why they matter for today’s telecom networks.
What is NFV?
Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) is a technology that allows traditional network services to run as software instead of relying on physical hardware. In the past, telecom networks depended on dedicated devices such as firewalls, load balancers, or routers. NFV replaces these devices with virtual network functions (VNFs) that run on standard servers.
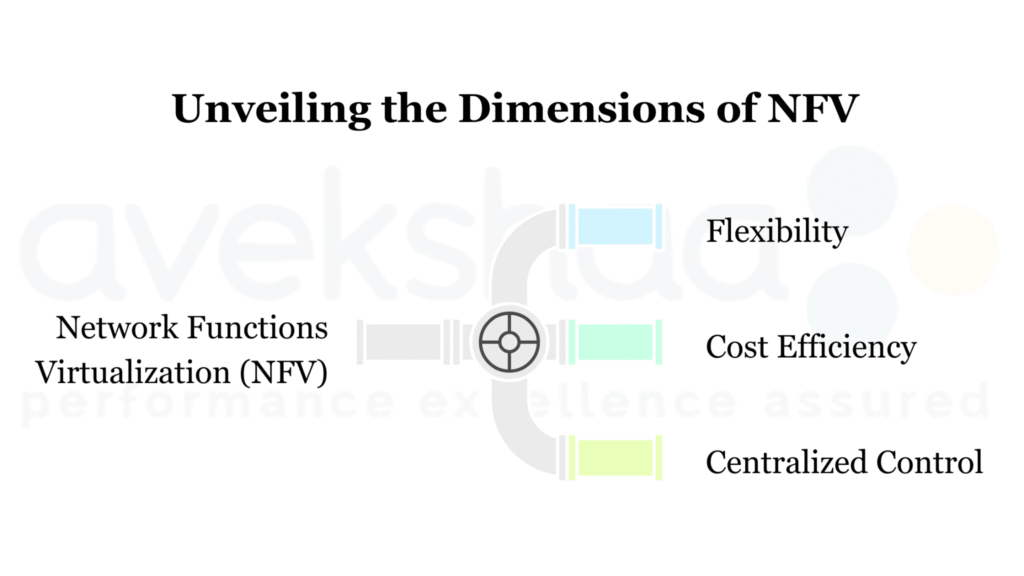
The main benefits of NFV include:
- Flexibility: VNFs can be deployed, updated, or removed quickly without changing physical hardware.
- Cost efficiency: Reducing the reliance on specialized hardware lowers both capital and operational costs.
- Simplified network management: Centralized software-based control makes it easier to manage network resources.
NFV Architecture
NFV works using three main components:
- NFV Infrastructure (NFVI): This includes the physical servers, storage, and networking resources where VNFs run.
- Management and Orchestration (MANO): MANO handles deploying, scaling, and monitoring VNFs. It ensures that network services run efficiently.
- Virtual Network Functions (VNFs): These are the actual network services, such as virtual routers, firewalls, or load balancers, running as software.
By virtualizing network functions, NFV allows telecom operators to react faster to market changes and reduce costs. However, as networks become more complex, NFV alone may not be enough.
What are Cloud-Native Network Functions (CNFs)?
Cloud-Native Network Functions (CNFs) build on the idea of NFV but take it further. CNFs are designed for cloud-native architectures. They use microservices, containers, and orchestration tools like Kubernetes to deliver network services more efficiently.
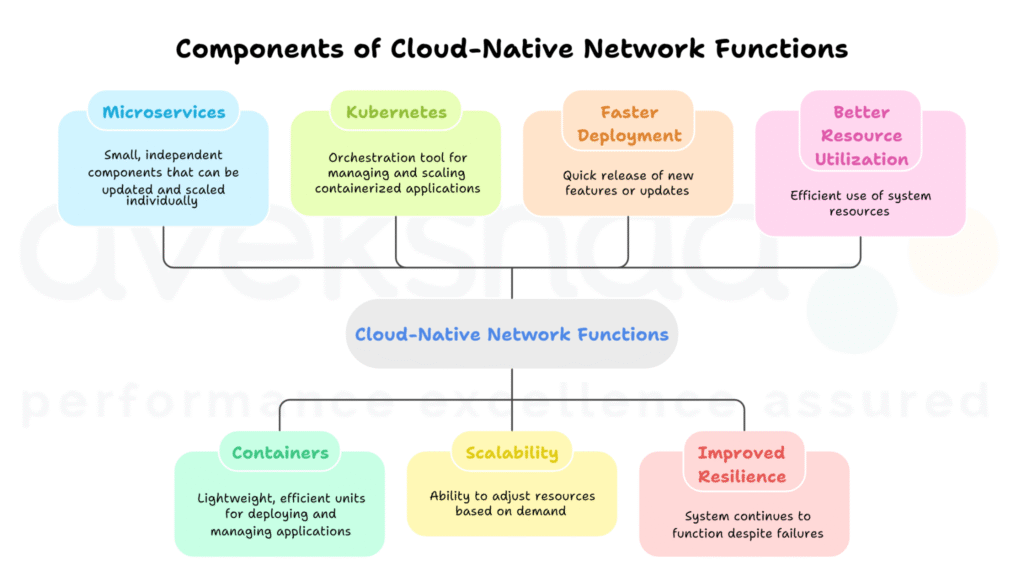
Unlike VNFs, which often run in virtual machines, CNFs are broken down into smaller components called microservices. These microservices can be updated, scaled, and deployed independently. This approach brings several benefits:
- Scalability: Microservices can scale up or down based on demand.
- Faster deployment: New features or updates can be released quickly.
- Improved resilience: If one microservice fails, the rest of the system continues to work.
- Better resource utilization: Containers are lightweight and use system resources more efficiently than traditional VMs.
CNFs are becoming essential for modern networks, especially with the rise of 5G, edge computing, and dynamic network services.
NFV vs CNF: Key Differences
Understanding the differences between NFV and CNF can help organizations decide which approach to adopt. Here’s a simple comparison:
| Feature | NFV | CNF |
| Deployment | Virtual machines | Containers |
| Architecture | Monolithic VNFs | Microservices-based |
| Scalability | Limited to VM resources | Highly scalable through microservices |
| Deployment Speed | Moderate | Fast |
| Resource Efficiency | Moderate | High |
| Orchestration | NFV MANO | Kubernetes and cloud-native tools |
In simple terms, NFV virtualizes the network, while CNFs optimize it for cloud environments. CNFs are more flexible, faster, and better suited for large-scale, dynamic networks.
Why CNFs Matter for Modern Telecom Networks
The telecom landscape is changing rapidly. Customers expect faster services, lower latency, and high reliability. CNFs provide the tools to meet these demands:
- Faster service rollout: New services can be deployed in hours instead of weeks.
- Automation and orchestration: CNFs integrate easily with modern automation tools, allowing network teams to manage services efficiently.
- Cost optimization: Lightweight containers reduce hardware and energy costs.
- High reliability: Microservices architecture ensures that individual failures do not disrupt the entire network.
By adopting CNFs, operators can prepare their networks for 5G, edge computing, and other future technologies.
Challenges and Considerations
While CNFs offer many benefits, migrating from NFV to CNFs is not without challenges:
- Migration complexity: Moving from virtual machines to containers requires careful planning.
- Skill requirements: Teams need knowledge of containerization, Kubernetes, and cloud-native technologies.
- Security: New architectures may introduce new security challenges that must be addressed.
- Orchestration tools: Managing CNFs requires modern orchestration tools, which may be new for some organizations.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of CNFs make them a worthwhile investment for future-ready networks.
How We Help with Modern Telecom Infrastructure
At our company, we support organizations in adopting modern telecom technologies, including NFV and CNFs. Our services include:
- Network monitoring and performance management: Ensuring your network runs smoothly at all times.
- Cloud solutions: Helping organizations migrate to cloud-native architectures efficiently.
- Consulting and implementation: Guiding businesses through NFV and CNF adoption with minimal disruption.
By partnering with us, you can leverage the advantages of modern network infrastructure while maintaining reliability, performance, and scalability.
The Future of Telecom Infrastructure
The evolution from NFV to CNFs is just one step in modernizing telecom networks. The future will likely include:
- 5G networks and network slicing: CNFs make it easier to deliver flexible, customized services.
- Edge computing: Deploying CNFs closer to users reduces latency and improves performance.
- AI and automation: Smart orchestration and monitoring will allow networks to self-optimize.
By adopting CNFs today, organizations can be ready for the networks of tomorrow.
Conclusion
NFV and CNFs have both played an important role in transforming telecom networks. NFV virtualized traditional network functions, making them more flexible and cost-efficient.
CNFs take this further with cloud-native architectures, microservices, and containers, enabling faster deployment, better scalability, and improved resilience.
Modern networks need to be agile, reliable, and ready for future technologies like 5G and edge computing. By leveraging CNFs and partnering with experts like us, organizations can ensure their networks are ready to meet today’s demands and tomorrow’s challenges.
Ready to modernize your network infrastructure? Visit us at Avekshaa to explore our network monitoring, cloud solutions, and consulting services. Let us help you build a scalable, high-performance, and future-ready telecom network.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
NFV is a technology that replaces traditional physical network devices with software-based virtual network functions (VNFs) running on standard servers, making networks more flexible and cost-efficient.
CNFs are network functions designed for cloud-native architectures. They use containers and microservices to improve scalability, speed of deployment, and resilience.
NFV runs network functions in virtual machines, while CNFs use containers and microservices. CNFs offer faster deployment, better scalability, and improved resource efficiency compared to NFV.
CNFs help telecom networks deploy new services faster, scale efficiently, and maintain high reliability, which is crucial for technologies like 5G and edge computing.
CNFs are gradually replacing VNFs in modern networks, but VNFs still exist in many legacy systems. Migration depends on network requirements and infrastructure.
Key benefits include faster deployment, better scalability, higher reliability, improved resource utilization, and easier automation and orchestration.
Challenges include migration complexity, need for new skills (containers, Kubernetes), security considerations, and managing orchestration tools.
Yes, CNFs are ideal for dynamic, high-performance networks like 5G and edge deployments due to their flexibility, speed, and microservices architecture.
No, CNFs run on standard servers or cloud infrastructure, just like NFV. Their container-based architecture is lightweight and efficient.
We provide network monitoring, cloud solutions, and consulting to guide organizations through NFV and CNF implementation, ensuring high performance, reliability, and future-ready networks.